Adding custom functions using "fn"
Occasionally, you may find opportunities to streamline your code by attaching new functionality to Knockout’s core value types. You can define custom functions on any of the following types:
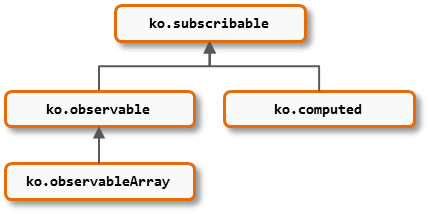
Because of inheritance, if you attach a function to ko.subscribable, it will be available on all the others too. If you attach a function to ko.observable, it will be inherited by ko.observableArray but not by ko.computed.
To attach a custom function, add it to one of the following extensibility points:
ko.subscribable.fnko.observable.fnko.observableArray.fnko.computed.fn
Then, your custom function will become available on all values of that type created from that point onwards.
Note: It’s best to use this extensibility point only for custom functions that are truly applicable in a wide range of scenarios. You don’t need to add a custom function to these namespaces if you’re only planning to use it once.
Example: A filtered view of an observable array
Here’s a way to define a filterByProperty function that will become available on all subsequently-created ko.observableArray instances:
ko.observableArray.fn.filterByProperty = function(propName, matchValue) {
return ko.pureComputed(function() {
var allItems = this(), matchingItems = [];
for (var i = 0; i < allItems.length; i++) {
var current = allItems[i];
if (ko.unwrap(current[propName]) === matchValue)
matchingItems.push(current);
}
return matchingItems;
}, this);
}
This returns a new computed value that provides a filtered view of the array, while leaving the original array unchanged. Because the filtered array is a computed observable, it will be re-evaluated whenever the underlying array changes.
The following live example shows how you could use this:
All tasks ( )
Done tasks ( )
Source code: View
<h3>All tasks (<span data-bind="text: tasks().length"> </span>)</h3>
<ul data-bind="foreach: tasks">
<li>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" data-bind="checked: done" />
<span data-bind="text: title"> </span>
</label>
</li>
</ul>
<h3>Done tasks (<span data-bind="text: doneTasks().length"> </span>)</h3>
<ul data-bind="foreach: doneTasks">
<li data-bind="text: title"></li>
</ul>
Source code: View model
function Task(title, done) {
this.title = ko.observable(title);
this.done = ko.observable(done);
}
function AppViewModel() {
this.tasks = ko.observableArray([
new Task('Find new desktop background', true),
new Task('Put shiny stickers on laptop', false),
new Task('Request more reggae music in the office', true)
]);
// Here's where we use the custom function
this.doneTasks = this.tasks.filterByProperty("done", true);
}
ko.applyBindings(new AppViewModel());
It’s not mandatory
If you tend to filter observable arrays a lot, adding a filterByProperty globally to all observable arrays might make your code tidier. But if you only need to filter occasionally, you could instead choose not to attach to ko.observableArray.fn, and instead just construct doneTasks by hand as follows:
this.doneTasks = ko.pureComputed(function() {
var all = this.tasks(), done = [];
for (var i = 0; i < all.length; i++)
if (all[i].done())
done.push(all[i]);
return done;
}, this);